
401(k)是美國私營企業流行的退休賬戶,名字來源於IRC Section 401(k)。它是一種defined contribution plan。Defined contribution意指員工自主選擇存入金額(contribution),盈虧自負;與之相對的defined benefit plan則由公司負責的一個統籌賬戶,福利(benefit)是固定的,根據員工的工作年限等在其退休時以年金形式發放。
Section 401(k)在1978年由Revenue Act加入tax code。標題deferred arrangement,是指公司代員工從paycheck中扣除一部分存入,獲得延稅優惠,延至離職或退休後再取出。1980年,Ted Benna將此條重新解釋,設計了僱主匹配(employer match),以免稅和employer match激勵了員工存入的積極性。401(k)的名稱不脛而走,很快流行。
IRS在1981年頒佈了401(k)的regulation。2006年之後401(k)可以有Roth選項,此為Roth 401(k)。401(k)內部也在2010年後出現了in-plan Roth rollover。同時401(k)也可以向不同類型的IRA作rollover。這些發展生成了今天複雜的退休計劃結構。
本文介紹401(k)賬戶的主要結構以及基本的存入取出規則。
401(k) Subaccounts
常見的401(k)結構

如圖,最常見的401k結構包括了員工存入(employee contribution)以及僱主存入(employer contribution)。Employer contribution部分一定是稅前收入(pre-tax),而employee contribution則按401(k) plan有不同的選項。
在最常見的pre-tax 401(k) plan中,employee contribution也是pre-tax,我們將這種plan稱之為pre-tax 401(k),其稅務規則與traditional IRA類似,即存入免稅,取出收稅。網絡上401(k)的基礎性介紹大部分是關於pre-tax 401(k)。與IRA類似,員工也大都知曉employee contribution有一個”IRS limit”(在2022年是20500)。超過該限額會引起不必要的麻煩(後有專文介紹超出後的補救辦法)。
完整的401(k)結構

2006年以後,很多僱主開始提供Roth 401(k);一些401 (k) plan還有after-tax 401(k)。值得注意的是,Roth 401(k)與after-tax 401(k)並不是單獨的401(k) plan,它們是民間對401(k)內subaccount的通俗稱呼。
Roth 401(k)是401(k)中的一個subaccount,是Roth IRA與401 (k)的糅合體,存入稅後金額,(退休後)取出時免稅。
部分401(k) plan還提供after-tax subaccount。稅務規則上,讀者可以將存after-tax 401(k)類比為traditional IRA的non-deductible contribution:存入的稅後收入,取出有pro-rata rule,並且盈利部分屬於pre-tax,取出時繳收入稅。
可見,pre-tax/Roth/after-tax 401(k)的繳稅規則各不相同,但又處在同一個401(k) plan當中。401(k) record keeper負責將每個subaccount的存入記錄與盈利記錄清楚。從這一點說,俗名Roth 401(k)也有道理,只是在理解下文的elective deferral limit時可能造成誤解。
Contribution Limits

Elective deferral
坊間常說的401(k) contribution limit其實是elective deferral limit。
本文題圖所引的IRC Section 401(k)即表明401(k)最開始是一個延稅計劃。所謂elective deferral即員工自願繳納的延稅款。早期的401(k)計劃只有pre-tax contribution,則elective deferral = pre-tax contribution。2006年引入的Roth 401(k)其學名為designated Roth acccount,即將elective deferral的一部分指定為Roth contribution,所以pre-tax 401(k)與Roth 401(k)分享elective deferral的限額。After-tax account的出現早於pre-tax 401(k),當時的deferral專指pre-tax deferral,因此after-tax account雖也有部分延稅功能,但不計入elective deferral。
簡言之
elective deferral = pre-tax empolyee contribution + Roth 401 (k)
IRC Sec. 402(g)規定了elective deferral的限額(402(g) limit)。
Annual addition and catch up
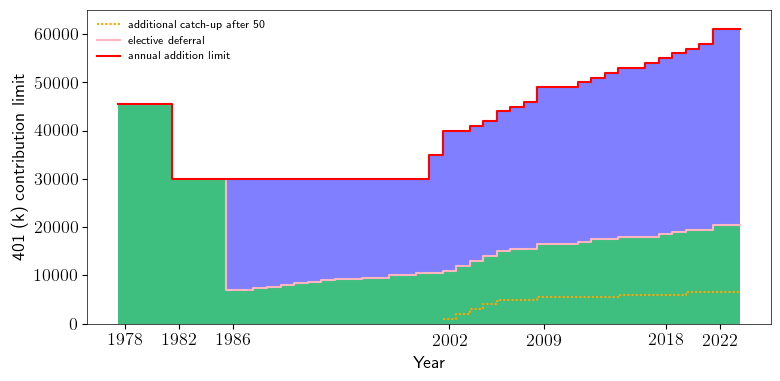
整個401(k)的存入金額稱為annual addition,它首先不能超過這份工作的總收入,其次IRC Sec. 415(c)規定了annual addition的限額(415(c) limit)。最後50歲以上的員工可以存catch-up contribution,這既不屬於elective deferral,也不屬於annual addition。
這些數值IRS每年會根據通脹調整,2022年的數值如下表
| elective deferral (employee contribution) | annual addition (total limit) | catch-up |
| 20500 | 61000 | 6500 |
根據這些限制,我們可以很容易計算出after-tax contribution limit
after-tax 401(k) limit = annual addition limit - elective deferral - empolyer match
歷年的數值如圖:
Multiple plans
擁有多位僱主或不同401(k) plan的朋友需注意,elective deferral統計所有qualified retirement plan (401(k),403(b)…),擁有多個plan不能增加elective deferral limit。2022年的總額為20500。但annual addition limit只適用於單個plan,有多個plan的讀者可以在每個plan存到annual addition limit,IRS給出了例子:
Example 1 : In 2019, Greg, 46, is employed by an employer with a 401(k) plan, and he also works as an independent contractor for an unrelated business and sets up a solo 401(k). Greg contributes the maximum amount to his employer』s 401(k) plan for 2019, $19,000. He would also like to contribute the maximum amount to his solo 401(k) plan. He is not able to make further elective deferrals to his solo 401(k) plan because he has already contributed his personal maximum, $19,000. He would also like to contribute the maximum amount to his solo 401(k) plan.
在這個例子中Greg擁有兩個401(k) plan。其中一個存滿了2019年的elective deferral limit,因此在另一個plan中他無法再存入elective deferral,但可以存elective deferral之外的部分。
However, he has enough earned income from his business to contribute the overall maximum for the year, $56,000. Greg can make a nonelective contribution of $56,000 to his solo 401(k) plan. This $56,000 limit is not reduced by the elective deferrals Greg made under his employer』s plan because the limit on annual additions applies to each plan separately.
這個例子中Greg為他自己的solo 401(k)存入了non-elective contribution,這是他作為self-empolyment僱主身份存入的employer contribution,並不是作為員工身份存入的elective deferral,所以仍然可以在該solo 401 (k) 內存到該plan的annual addition limit。
值得注意的是,annual additions applies to each plan separately的條件是401(k) plan的主體之間沒有legal overlap or affiliated relationship。很多情況可以通過常識判斷(例如同一僱主或子公司),更精確的定義以及複雜的情況請諮詢律師。
Employer Contribution
僱主存入可分為employer match和nonelective contribution。前者是401(k)的發明,僱主的存入按一定規則匹配員工的存入,從而鼓勵員工使用該401(k) plan。後者的稱謂nonelective與elective deferral相對,表示這不由員工,而完全由僱主決定。這一類employer contribution,員工即使不存elective deferral,僱主也會存入。
Vesting schedule
「Vesting」 in a retirement plan means ownership. -- by IRS
員工存入401(k)的資金會立即100% vest,即將所有權轉讓給401(k)這個trust(由trustee代管,401(k)的creditor protection即來自於此安排)。
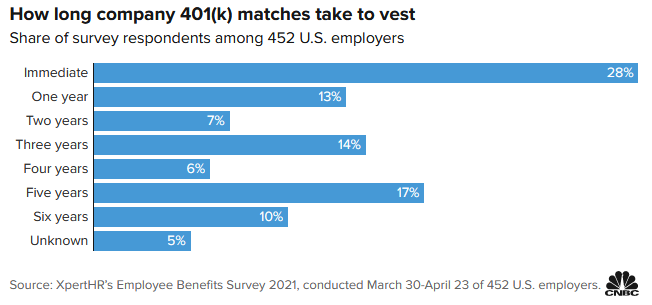
但employer contribution的所有權從僱主轉到401(k)則可能需要等待一段時間(例如兩年),這即是vesting schedule,拿過RSU的讀者應該不陌生。根據CNBC報道,只有28%的僱主提供100% immediate vesting。
IRC Sec. 411規定了minimal vesting schedule。對於401(k)這樣的define contribution plan,最低要求是3-year vesting 或者2 to 6 year vesting。IRS將這兩種vesting schedule稱為cliff vesting和graded vesting:
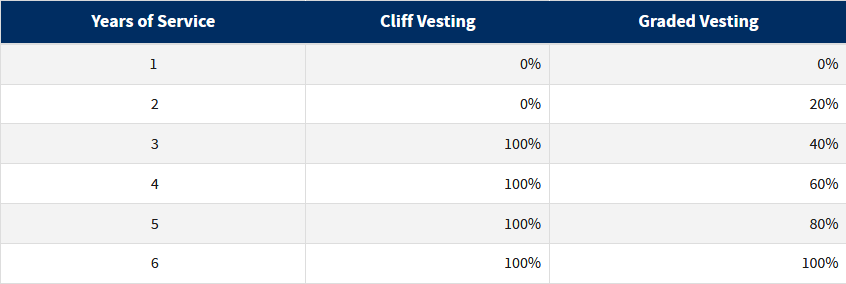
由表可知,對於cliff vesting,入職前兩年是拿不到絲毫employer contribution的。短期內打算跳槽的朋友,弄清vesting schedule後再決定是否存401(k)。
Forfeiture
在尚未達到100% vested時離職了,那麼employer contribution中non-vested部分怎麼處理呢?
這部分employer contribution暫時不屬於員工,但僱主也不能立即收回。這筆錢會繼續存在於401(k)中,直到滿足forfeiture的條件。這些條件可以是如下任何一個:
- 員工將整個401(k) plan rollover至IRA,即vested部分的401(k)資金已清空
- 員工滿足IRC Sec. 410(a)(5)定義的break in service,例如連續5年沒有回到這家公司工作
滿足條件後,non-vested employer contribution變成forfeiture,僱主可將之收回,抵消401(k)費用,或作為employer contribution發給其他員工。
若有non-vested部分,且在短時間內有可能重回老東家可能性,可以考慮保留401(k),以便將來拿回這部分employer contribution。
Nondiscrimination tests
ADP/ACP tests
為了防止401(k)計划過於優待高收入員工,IRC Sec. 401(k)以及Sec 401(m)分別制定了兩種nondiscrimination test,稱為Actual Deferral Percentage (ADP) Test和Actual Contribution Percentage (ACP) Test。
這兩種測試首先將參與401(k)的員工分成高收入人群和低收入人群。要通過ADP test,高收入員工elective deferral的比例和總量不能超過低收入員工太多;而ACP test則是類似的對兩類員工employer contribution或者after-tax contribution比例和總量的要求。可見這兩個測試覆蓋了401(k)內的各個子賬戶。具體的標準可參考IRS和investopedia的介紹文章。
ADP/ACP可能會產生額外的401(k)存入限制
以上雖然401(k) plan是對僱主的要求,但僱主為了通過nondiscrimination test,其補救和預防措施(參考IRS網頁)也會間接影響到員工福利。
首先,假如一個401(k) plan當年沒有通過nondiscrimination test,則僱主可以選擇給低收入員工做nonelective contribution,用增加employer contribution的方式通過test。當然,僱主也可以選擇退回部分高收入員工的存入款,給他們做一次corrective distribution。
其次,nondiscrimination test每一年都會評估一次。僱主為了通過測試,可能會對高收入員工的401(k) contribution設額外的限制,即高收入員工可能無法存滿稅法規定的elective deferral和annual addition limit。一些公司的401(k) plan不設置after-tax 401(k)可能也出於通過ACP test的考慮。
最後,僱主可能會選擇免於ADP/ACP test的safe harbor 401(k) plan。作為交換,safe harbor plan的條件是100% immediate vest(即沒有vesting schedule)。同時employer contribution必須在safe harbor plan指定的三種方式中選一種(大約是至少工資4%的employer match或者3%的nonelective contribution,具體可參考此文)。
名詞辨析:traditional 401(k)
一部分網站仿照traditional IRA,將pre-tax 401(k)稱為traditional 401(k)。
這會造成名字衝突。
根據IRS的命名,traditional 401(k)是指employer match可以有vesting schedule,同時必須通過ADP/ACP test的401(k) plan。與之相對的概念不是Roth 401(k),而是safe harbor 401(k)。

本文所指的pre-tax 401(k)其實是401(k)內的兩個subaccount,一個是(已經vest的)employer contribution,一個是pre-tax employer contribution。
故而Rollover式子
pre-tax 401(k) -> traditional IRA
表示將這兩部分pre-tax money轉到traditional IRA中。
Distribution
401(k) plan中各subaccount的取錢規則稍有不同,我們之後分節介紹。其中elective deferral的部分在Sec. 401(k)(2)(B)(i)統一限制了取出條件,不得早於
- 員工離職,去世或殘疾
- 員工年齡達到59.5歲
- 其他一些hardship條件等
以上條件是「或」的關係。由此可以推斷,員工離職前一般無法取出elective deferral(注意,即使願意交罰款也不行);但若達到59.5歲仍在工作,則在plan允許的情況下可以。
59.5歲是最常見的qualified distribution條件,不達該年齡從401(k)中取錢,計算收入稅的部分會有10%的罰金。IRA, 401(k)的罰金規則統一定義在Sec. 72(t),所以這一罰金規則是類似的。
Rule of 55
此為Sec. 72(t)罰金規則的一種例外情況。員工若在滿55歲或以上的那一年離職,那麼從離職僱主處的401(k)取錢,可免去10%的罰金。員工離職後可以找其他工作。
本規則可用於提早5年退休取錢,今後有專文配合案例分析。
Required minimal distribution (Sec. 401(a)(9))
401(k) plan (包括pre-tax/Roth/after-tax)與 traditional IRA 一樣,在持有人年齡超過72歲時,須按照IRS提供的預期壽命表格計算每年最低取出的比例,少取部分有50%的罰金。
Creditor Protection
Creditor protection或者asset protection是指財產在訴訟中被保護不受清算的影響。
401(k)內的財產在取出前,所有權屬於401(k) trust。1974年通過的Employee Retirement Income Security Act(ERISA)為401(k)這樣的qualified retirement plan提供了creditor protection。其Sec. 206(d)(1)的anti-alienation provision規定了401(k)內的財產不可轉移給第三方。
ERISA protection幾乎能擋住所有的債主,明顯的例外只有兩個:IRS和離婚時的配偶。
在執行rollover時
401(k) -> IRA
ERISA對bankrupacy creditor的保護被IRA繼承,但對non-bankrupacy creditor的保護則受州法律限制,在大部分州仍然是繼承的。
總而言之,401(k)與IRA的creditor protection級別都很高,差別不大。
總結
本文介紹了401(k) plan的總體結構。
為了弄清楚401(k)的contribution limit,我們先介紹了401(k)內部的pre-tax/Roth/after-tax subaccounts,然後引出了elective deferral和annual addition這些概念。對於contribution limit來說,nondiscriminative test引導僱主的調整也可能引入其他的存入限制。
Employer contribution需注意vesting schedule。在入職前預估vested部分,規劃401(k)存入量。在離職時考慮non-vested部分及未來回到該公司的可能性。
結尾,我們簡述了ERISA為401(k)提供的creditor protection。
參考資料:Publication 7334, IRS 401k overview, EmployeeFiduciary: 401k contribution, ACP/ADP(Forbes), investopedia: creditor protection, irahelp:creditor protection

免責聲明:本文及其中任何文字均僅為一般性的介紹,絕不構成任何法律意見或建議,不得作為法律意見或建議以任何形式被依賴,我們對其不負擔任何形式的責任。我們強烈建議您,若有稅務問題,請立即諮詢專業的稅務律師或稅務顧問。
Disclaimer: This article and any content herein are general introduction for readers only, and shall not constitute nor be relied on as legal opinion or legal advice in any form. We assume no liability for anything herein. If you need help about tax, please talk to a tax, legal or accounting advisor immediately.
